Discover how HTML directly impacts your website’s SEO performance. Learn essential HTML tags like <title>, <meta>, <header>, and <schema> that boost search rankings, improve crawlability, and enhance rich snippets. We’ll analyze common HTML mistakes harming visibility and provide actionable fixes to align your code with Google’s guidelines. Perfect for developers and marketers aiming to merge technical SEO with frontend best practices. ❤️
Key Concepts Of HTML
Before exploring how HTML affects SEO, it’s important to understand the core concepts: HTML tags, HTML elements, HTML attributes, and Meta elements. While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they have distinct roles in web development and search engine optimization.
HTML Tags
Definition: HTML tags are the basic markup symbols used to define content in a web page. They are enclosed in angle brackets < > and usually come in pairs (opening and closing tags), though some are self-closing (e.g., <img>).
Format:
- Opening tag:
<tagname>(e.g.,<p>) - Closing tag:
</tagname>(e.g.,</p>) - Self-closing tag:
<tagname />or<tagname>(e.g.,<br>or<img src="image.jpg">)
Example:
<h1>This is a heading</h1> <!-- <h1> and </h1> are tags -->
<img src="logo.png" alt="Website logo"> <!-- <img> is a self-closing tag -->
SEO Relevance: Search engines rely on HTML tags to understand page structure. For example, <h1> to <h6> tags help identify heading hierarchy, while <a> tags define hyperlinks, influencing page ranking signals.
Meta Elements
Definition: Meta elements are special HTML tags that provide metadata (information about the webpage). They are placed in the <head> section and are not displayed on the page but are critical for SEO.
Note: “Meta tags” is the common term for <meta> markup in daily use, while “Meta elements” is the more technical term used in formal specifications, though both refer to the same HTML metadata tags.
Format:
<meta name="description" content="Page description">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
Example:
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="description" content="A tutorial on HTML and SEO">
<meta name="keywords" content="HTML, SEO, Search Engine Optimization">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
</head>
SEO Relevance:
<meta name="description">influences the snippet shown in search results.<meta charset="UTF-8">ensures proper text encoding.<meta name="viewport">affects mobile-friendliness, a Google ranking factor.
HTML Elements
Definition: An HTML element consists of an opening tag, content (optional), and a closing tag. In other words, an element = opening tag + content + closing tag (or just a self-closing tag).
Format:
<tagname>Content</tagname> <!-- Complete element -->
<tagname /> or <tagname> <!-- Self-closing element -->
Example:
<p>This is a paragraph.</p> <!-- A paragraph element -->
<a href="https://example.com">Click here</a> <!-- A link element -->
SEO Relevance: Search engines analyze entire HTML elements, not just tags. For instance:
- The
<title>element directly impacts how search engines interpret the page’s topic. - The
<a>element includes both the link (href) and anchor text, affecting SEO ranking signals.
HTML Attributes
Definition: HTML attributes provide additional information or settings for an element. They are always placed inside the opening tag in a name="value" format.
Format:
<tagname attribute1="value1" attribute2="value2">Content</tagname>
Example:
<img src="photo.jpg" alt="Scenery" width="500"> <!-- src, alt, width are attributes -->
<a href="https://example.com" target="_blank">Visit Example</a> <!-- href and target are attributes -->
SEO Relevance:
- The
altattribute helps search engines understand images (important for image SEO). - The
hrefattribute determines link destinations, affecting crawling and ranking. - The
rel="nofollow"attribute tells search engines not to follow certain links.
Meta Tags and Their SEO Impact
Title Tag: Your Search Result Headline
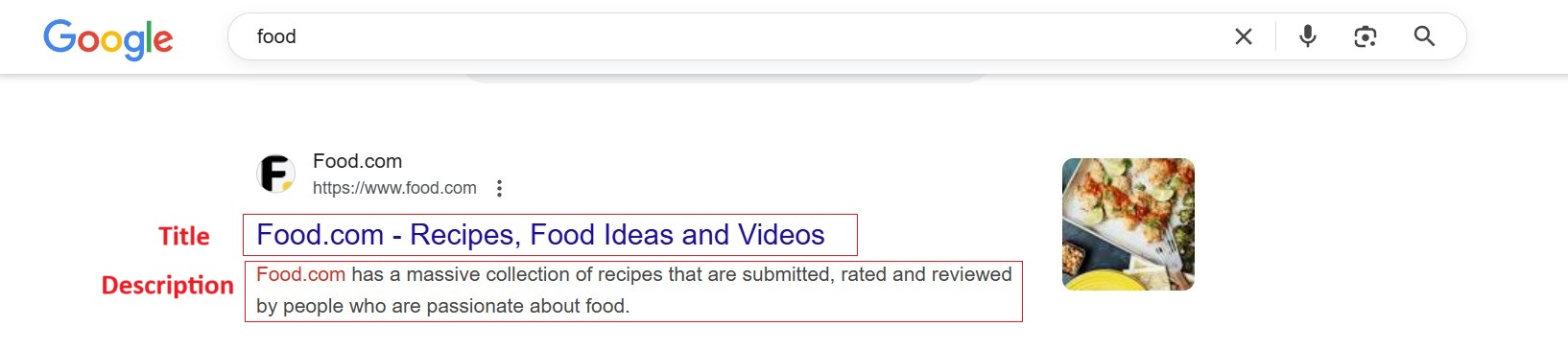
The <title> tag defines what appears as the clickable headline in search results. It’s a key SEO factor—affecting rankings and click-through rates (CTR).
Key Rules for Effective Title Tags
- Length: Keep under 60 characters to avoid truncation
- Keywords: Place main keywords near the front
- Uniqueness: Every page should have a distinct title
- Readability: Avoid spammy keyword stuffing
Example (Good vs. Bad)
✅ Good:
<title>Best Wireless Headphones 2024 - Expert Reviews</title>
❌ Bad:
<title>Headphones | Buy Headphones | Cheap Headphones | Best Headphones 2024</title>
Pro Tips
- Include your brand name at the end if space allows
- Use pipes (
|) or hyphens (-) to separate phrases - Test different titles in Google Search Console
Meta Description: Controlling SERP Snippets

The <meta name="description"> tag provides a concise summary of your webpage’s content that appears in search results. While it doesn’t directly impact rankings, it significantly influences click-through rates (CTR) by helping users understand what your page offers.
Key Characteristics of Effective Meta Descriptions
- Optimal length: 150-160 characters (truncated beyond this)
- Clear value proposition: Explain why users should click
- Keyword inclusion: Naturally incorporate target keywords
- Active language: Use action-oriented verbs
- Uniqueness: Each page should have a distinct description
Code Example
<meta name="description" content="Discover the best coffee brewing techniques for home baristas. Learn French press, pour-over, and espresso methods with our step-by-step guides.">
Best Practices
- Write compelling copy that stands out in SERPs
- Match search intent by addressing user queries
- Include a call-to-action when appropriate (“Learn more”, “Get started”)
- Avoid duplication across pages
- Don’t over-optimize - keep it natural and readable
Good vs Bad Examples
✅ Effective: “Learn professional photography lighting techniques with our free online course. Perfect for beginners starting their photography journey.”
❌ Ineffective: “Photography lighting course lighting techniques learn photography lighting professional lighting”
Additional Tips
- Google may rewrite descriptions if they don’t match search queries
- Consider including numbers or statistics when relevant
- Test different descriptions to see what generates higher CTR
- Use schema markup to enhance how your description appears
Remember: While meta descriptions don’t affect rankings, a well-written one can substantially improve your traffic by increasing CTR from search results. Treat it as your page’s advertisement in the SERPs.
Monitoring & Optimization
- Check Google Search Console for “meta description too short” warnings
- Review which pages are showing Google’s auto-generated descriptions
- A/B test different versions for important pages
- Update descriptions when content significantly changes
Viewport Tag: Essential for Mobile Friendliness
The viewport meta tag is a critical HTML element that controls how your website displays on mobile devices. It ensures proper scaling and responsive behavior, directly impacting both user experience and mobile SEO performance.
Core Functionality
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
This standard implementation:
- Sets width to match device width
- Establishes 1:1 scale ratio
- Prevents unwanted zooming behavior
Why It Matters for SEO
- Mobile-first indexing: Google primarily uses mobile version for ranking
- Bounce rate reduction: Proper mobile display keeps users engaged
- Core Web Vitals: Affects loading and visual stability metrics
Key Parameters
| Parameter | Effect | Recommended Value |
|---|---|---|
| width | Content width | device-width |
| initial-scale | Starting zoom level | 1.0 |
| minimum-scale | Minimum zoom allowed | 1.0 |
| maximum-scale | Maximum zoom allowed | 1.0 |
| user-scalable | Allow zooming | no (use carefully) |
Best Practices
- Always include in the
<head>section - Avoid disabling zoom unless absolutely necessary (accessibility concern)
- Combine with responsive design using CSS media queries
- Test thoroughly across different devices
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- ❌ Omitting the viewport tag entirely
- ❌ Setting fixed width (e.g., content=“width=1200”)
- ❌ Disabling zoom without accessibility alternatives
- ❌ Using inconsistent scale values
Troubleshooting Tips
- Use Chrome DevTools device mode to test responsiveness
- Check Google Search Console’s Mobile Usability report
- Validate with W3C mobileOK Checker
- Monitor Core Web Vitals metrics
Advanced Implementation
For progressive web apps (PWAs):
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, minimum-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no, viewport-fit=cover">
Robots Meta: Directing Crawlers
The robots meta tag gives webmasters precise control over how search engine crawlers interact with webpage content. Unlike robots.txt which works at directory level, this HTML element provides page-specific indexing instructions.
Basic Implementation
<meta name="robots" content="[directives]">
Common Directives
| Directive | Function | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| index | Allow indexing | Standard pages |
| noindex | Block indexing | Private/duplicate content |
| follow | Follow links | Most pages |
| nofollow | Don’t follow links | Untrusted UGC |
| noarchive | Prevent caching | Time-sensitive content |
| nosnippet | Block snippets | Copyrighted text |
| max-image-preview | Image preview control | Image-heavy pages |
Key Considerations
- Implementation Depth:
- Works at individual page level
- Overrides robots.txt instructions
- Takes precedence over canonical tags
- SEO Impact:
- Critical for duplicate content management
- Essential for crawl budget optimization
- Affects indexation speed (noindex pages get crawled less)
- Common Applications:
- Paginated series (noindex follow)
- Thank you pages
- Search result pages
- Staging/development versions
Best Practices
- Place in
<head>section for proper interpretation - Use X-Robots-Tag for non-HTML files (PDFs, images)
- Combine with HTTP headers for maximum control
- Monitor via Search Console for unintended blocking
Charset Declaration: Ensuring Proper Rendering
The charset meta tag is a fundamental HTML element that specifies the character encoding for a webpage. This declaration ensures text displays correctly across all browsers and devices, preventing rendering issues like garbled characters.
Standard Implementation
<meta charset="UTF-8">
Best Practices
-
Placement Priority:
- Must appear within first 1024 bytes
- Should be the first element in
<head> - Example of ideal placement:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <!-- Other meta tags --> -
Configuration Options:
- For legacy HTML4:
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">- For XML/XHTML:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
SEO Implications
- Affects readability of multilingual content
- Impacts rich snippet display
- Essential for international SEO
- Helps prevent duplicate content issues from encoding errors
Validation Tools
- Browser “View Page Source”
- W3C Validator
- Web Developer extension (Encoding menu)
- Chrome DevTools Network panel
Canonical Tag: Solving Duplicate Content Issues
The canonical tag (rel="canonical") is a critical HTML element that helps search engines understand which version of a page should be considered “original” when duplicate or similar content exists across multiple URLs.
Basic Implementation
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/preferred-url">
Core Functions
- Duplicate Content Resolution:
- Tells search engines which URL to index
- Consolidates ranking signals to preferred version
- Prevents self-competition in search results
- URL Normalization:
- Handles parameters (?sessionid=123)
- Manages protocol variants (HTTP/HTTPS)
- Resolves www/non-www discrepancies
Common Use Cases
| Scenario | Implementation Example |
|---|---|
| Pagination | <link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/blog?page=1"> |
| Product variants | <link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/product?color=red"> |
| Session IDs | <link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/product"> |
| Printer-friendly | <link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/article"> |
Best Practices
-
Self-referencing Canonicals:
- Every page should reference itself as canonical
- Even if no duplicates exist
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/current-page"> -
Absolute URLs:
- Always use full URLs (including https://)
- Avoid relative paths (/page.html)
-
Single Canonical:
- Only one canonical tag per page
- Multiple tags confuse search engines
Technical Considerations
- Implementation Methods:
- HTML tag (most common)
- HTTP header (for non-HTML files)
- JavaScript injection (when needed)
- Crawlability:
- Canonical URL must be crawlable
- Should return 200 status code
- Must not be blocked by robots.txt
Common Mistakes
- ❌ Pointing to a 404 page
- ❌ Creating canonical loops (A→B→A)
- ❌ Using non-indexable URLs as canonical
- ❌ Canonicalizing to different domain without redirect
Advanced Applications
-
Cross-Domain Canonicals:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://anotherdomain.com/original-content">(Use with caution - requires proper verification)
-
Hreflang Integration:
- Canonicals work with hreflang tags
- Each language version needs its own canonical
Verification & Testing
- Google Search Console:
- Index Coverage report
- URL Inspection tool
- SEO Audit Tools:
- Screaming Frog
- DeepCrawl
- Sitebulb
- Browser Testing:
- View page source
- Check network requests
Social Media Meta (Open Graph/Twitter Cards)
Social media meta tags control how your content appears when shared on platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter. These tags don’t affect SEO directly, but they significantly impact click-through rates from social networks.
Core Tag Groups
- Open Graph (Facebook/LinkedIn)
<meta property="og:title" content="Page Title">
<meta property="og:description" content="Page description">
<meta property="og:image" content="https://example.com/image.jpg">
<meta property="og:url" content="https://example.com/page">
<meta property="og:type" content="website">
<meta name="twitter:card" content="summary_large_image">
<meta name="twitter:title" content="Page Title">
<meta name="twitter:description" content="Page description">
<meta name="twitter:image" content="https://example.com/image.jpg">
<meta name="twitter:site" content="@yourhandle">
Critical Components
- Visual Elements
- Image size: 1200×630 pixels (recommended)
- File type: JPG or PNG
- File size: Under 1MB
- Content Optimization
- Title: ≤ 60 characters
- Description: ≤ 200 characters
- URL: Canonical version
Best Practices
- Always Include
- og:title
- og:description
- og:image
- og:url
- twitter:card
- Platform-Specific Notes
- Facebook: Prefers Open Graph
- Twitter: Reads Twitter Cards first, falls back to OG
- LinkedIn: Uses Open Graph exclusively
- Image Guidelines
- Use high-quality, relevant images
- Include text overlay when appropriate
- Avoid stock photo clichés
Implementation Checklist
- Basic Tags
<!-- Essential Open Graph -->
<meta property="og:title" content="Your Content Title">
<meta property="og:description" content="Your engaging description">
<meta property="og:image" content="https://example.com/social-image.jpg">
<meta property="og:url" content="https://example.com/your-page">
<!-- Twitter Card -->
<meta name="twitter:card" content="summary_large_image">
<meta name="twitter:creator" content="@authorhandle">
- Advanced Tags
<!-- Article Specific -->
<meta property="article:published_time" content="2023-01-01T00:00:00+00:00">
<meta property="article:author" content="Author Name">
<!-- Video Content -->
<meta property="og:video" content="https://example.com/video.mp4">
Common Mistakes
- ❌ Using different content for OG and Twitter
- ❌ Missing image alt text for accessibility
- ❌ Using non-absolute URLs
- ❌ Forgetting to update when content changes
Debugging Tools
- Facebook Sharing Debugger
- Tests OG tags
- Clears cache
- Provides preview
- Twitter Card Validator
- Displays card preview
- Identifies errors
- LinkedIn Post Inspector
- Checks link previews
- Shows potential issues
Performance Tips
- Pre-cache Your Links
- Submit to platforms before sharing
- Ensures proper rendering
- Dynamic Generation
- CMS plugins
- Server-side rendering
- CDN optimization
- Monitoring
- Track social engagement
- A/B test different images
- Update regularly
HTML Structure and Semantic Elements
Heading Hierarchy (H1-H6): Content Organization
Heading tags (H1-H6) form the structural backbone of your HTML document, serving as both an accessibility aid and a content organization signal for search engines. Proper heading hierarchy helps users and crawlers understand your page’s information architecture.
Core Implementation Rules
- Hierarchy Structure
<h1>Main Page Title</h1>
<h2>Primary Section</h2>
<h3>Subsection</h3>
<h3>Subsection</h3>
<h4>Detail Point</h4>
<h2>Secondary Section</h2>
- Key Requirements
- Single H1 per page (except for HTML5 document outlines)
- Logical nesting order (never skip levels)
- Semantic relevance to content
SEO Best Practices
- Content Optimization
- Front-load keywords in higher-level headings
- Keep headings concise (≤ 70 characters)
- Match search intent in H2s/H3s
- Technical Considerations
- Avoid using headings for stylistic purposes
- Don’t hide headings with CSS
- Maintain text-to-heading ratio (3-5 headings per 1000 words)
Common Patterns
- Article Structure
<h1>How to Bake Sourdough Bread</h1>
<h2>Ingredients Needed</h2>
<h2>Step-by-Step Instructions</h2>
<h3>Preparing the Starter</h3>
<h3>First Rise</h3>
<h4>Ideal Temperature Conditions</h4>
- Product Pages
<h1>Wireless Headphones Pro X</h1>
<h2>Key Features</h2>
<h2>Technical Specifications</h2>
<h3>Battery Life</h3>
<h3>Noise Cancellation</h3>
Common Mistakes
- ❌ Using multiple H1 tags unnecessarily
- ❌ Skipping heading levels (H2 → H4)
- ❌ Using headings for non-heading content
- ❌ Keyword stuffing in headings
- ❌ Duplicate heading text across pages
Performance Impact
- Page Speed
- Keep heading text lightweight
- Avoid complex selectors in CSS
- Minimize heading-related JavaScript
- Crawl Efficiency
- Clear structure helps bot understanding
- Important content should appear early in hierarchy
- Supports featured snippet generation
Semantic HTML5 Tags (article, section, etc.)
Semantic HTML5 tags provide meaning to web content beyond just presentation, helping search engines and assistive technologies better understand your page structure.
Core Semantic Elements
<article>
<header>
<h1>Blog Post Title</h1>
</header>
<section>
<h2>Introduction</h2>
<p>Content...</p>
</section>
<footer>
<p>Posted on <time datetime="2023-05-15">May 15</time></p>
</footer>
</article>
Key Tags and Usage
| Tag | Purpose | SEO Benefit |
|---|---|---|
<article> |
Self-contained composition | Identifies primary content |
<section> |
Thematic grouping | Organizes related content |
<header> |
Introductory content | Contains important H1s |
<footer> |
Closing content | Holds metadata |
<nav> |
Navigation links | Highlights site structure |
<aside> |
Complementary content | Identifies secondary info |
<figure> + <figcaption> |
Media with caption | Improves image context |
<time> |
DateTime information | Supports rich snippets |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- ❌ Using
<div>when semantic tags exist - ❌ Nesting
<article>inside<article>without purpose - ❌ Using
<section>without headings - ❌ Misusing
<aside>for primary content
Accessibility Benefits
- 40% better screen reader navigation
- Improved keyboard navigation
- Better landmark identification
SEO Advantages
- Clear content segmentation
- Enhanced crawl efficiency
- Support for rich results
Image Optimization with Alt Text
Core Concept
The alt attribute provides textual descriptions of images for:
- Search engine crawlers (SEO value)
- Screen readers (accessibility compliance)
- Fallback display when images fail to load
Technical Implementation
<img src="coffee-beans.jpg" alt="Fresh Arabica coffee beans on wooden table" width="800" height="600" loading="lazy">
SEO Best Practices
- Content Guidelines
- Be specific but concise (6-10 words ideal)
- Include target keywords naturally
- Describe both subject and context
- Avoid “image of” or “picture of” redundancy
- Special Cases
<!-- Decorative images -->
<img src="divider.png" alt="" role="presentation">
<!-- Complex infographics -->
<img src="chart.jpg" alt="[Detailed description below]">
<details>
<summary>Image Description</summary>
<p>Bar chart showing coffee consumption trends...</p>
</details>
Common Mistakes
- ❌ Empty alt text for informative images (
alt="") - ❌ Keyword stuffing (
alt="coffee beans buy best arabica cheap organic") - ❌ Duplicate alt text across images
- ❌ Omitting width/height attributes
Advanced Optimization
- Image Filenames
<!-- Bad -->
<img src="IMG_1234.jpg" alt="">
<!-- Good -->
<img src="organic-arabica-coffee-beans.jpg" alt="Organic Arabica coffee beans">
- Responsive Images
<picture>
<source media="(min-width: 800px)" srcset="coffee-beans-large.jpg">
<source media="(min-width: 400px)" srcset="coffee-beans-medium.jpg">
<img src="coffee-beans-small.jpg" alt="Coffee beans close-up">
</picture>
Performance Impact
- Lazy Loading
<img src="coffee.jpg" alt="Coffee cup" loading="lazy">
- Modern Formats
<img src="coffee.avif" alt="Coffee preparation" width="600" height="400">
Anchor Tags and Link Relationships
Core SEO Functionality
Anchor tags (<a>) and their rel attributes control link equity flow and establish content relationships. Proper implementation affects:
- PageRank distribution
- Crawl prioritization
- Content discoverability
- Spam prevention
Basic Implementation
<a href="https://example.com/guide" rel="[attributes]">Link Text</a>
Critical rel Attributes
| Attribute | Purpose | SEO Impact |
|---|---|---|
nofollow |
Blocks PageRank flow | Prevents spam (UGC/ads) |
sponsored |
Marks paid links | Compliance requirement |
ugc |
User-generated content | Identifies untrusted links |
noopener |
Security protection | Prevents tabnabbing |
noreferrer |
Holds referrer data | Privacy protection |
Best Practices
- Link Equity Management
<!-- Internal link (passes equity) -->
<a href="/blog/seo-tips">SEO Guide</a>
<!-- External nofollow -->
<a href="https://external.com" rel="nofollow">Partner Site</a>
- E-A-T Compliance
<!-- Sponsored content disclosure -->
<a href="https://partner.com" rel="sponsored">Sponsored Deal</a>
<!-- UGC in comments -->
<a href="https://user-site.com" rel="ugc nofollow">User's Blog</a>
Advanced Relationships
- Pagination Signals
<link rel="prev" href="/page1">
<link rel="next" href="/page3">
- Canonical Reinforcement
<a href="/product" rel="canonical">View Main Product</a>
- Resource Hints
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://cdn.example.com">
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//widgets.com">
Common Mistakes
- ❌ Overusing
nofollowinternally - ❌ Missing
relon sponsored links - ❌ Inconsistent link text
- ❌ Broken fragment identifiers (#)
- ❌ Orphaned links (no inbound links)
HTML Attributes That Boost SEO
Alt Attributes for Image Accessibility
Core Purpose
Alt attributes (alt) serve dual critical functions:
- Accessibility Foundation - Enables screen readers to convey visual content
- SEO Context - Provides search engines with image understanding
Technical Implementation
<img src="baking-supplies.jpg"
alt="Assorted baking tools on marble countertop"
width="1200"
height="800"
loading="lazy">
SEO-Specific Guidelines
- Keyword Optimization
- Front-load primary keywords
- Natural language flow
- Avoid keyword stuffing
<!-- Good -->
alt="Professional chef preparing sourdough bread"
<!-- Bad -->
alt="bread, sourdough, baking, chef, cook, bakery"
- E-Commerce Best Practice
<img src="running-shoes.jpg"
alt="Nike Air Zoom Pegasus 40 - Women's Cushioned Running Shoes (Blue/White)"
title="View product details">
Common Pitfalls
- ❌ Using “image of” or “picture of” redundancies
- ❌ Omitting alt for functional images (icons, buttons)
- ❌ Duplicating alt text across similar images
- ❌ Relying on title attributes as alternatives
Special Cases
- Decorative Images
<div class="divider">
<img src="ornament.png" alt="" role="presentation">
</div>
- Linked Images
<a href="/contact">
<img src="contact-icon.png" alt="Contact Us">
</a>
- SVG Implementation
<svg role="img" aria-label="Company logo">
<title>Acme Corporation</title>
<!-- SVG paths -->
</svg>
Performance Considerations
- Lazy Loading Integration
<img src="ingredients.jpg"
alt="Organic baking ingredients lineup"
loading="lazy"
width="800"
height="600">
- Modern Format Support
<img src="bread.avif"
alt="Freshly baked croissants on rack"
type="image/avif">
Rel Attributes for Link Context (nofollow, sponsored)
Core SEO Functionality
The rel attribute in anchor tags (<a>) controls how search engines interpret and value links. These attributes directly impact:
- PageRank distribution
- Crawl budget allocation
- Spam prevention
- Legal compliance (FTC disclosure requirements)
Essential Rel Values
| Attribute | Purpose | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
nofollow |
Blocks link equity flow | User-generated content, untrusted links |
sponsored |
Identifies paid placements | Ads, sponsored posts, affiliate links |
ugc |
Marks user-generated links | Comments, forum posts, reviews |
noopener |
Security protection | All target="_blank" links |
noreferrer |
Hides referrer data | Privacy-sensitive links |
Implementation Guide
- Basic Link Markup
<!-- Standard follow link -->
<a href="/resources">Learn More</a>
<!-- Nofollow external link -->
<a href="https://external.com" rel="nofollow">Reference</a>
<!-- Sponsored disclosure -->
<a href="https://partner.com" rel="sponsored">Our Sponsor</a>
- Combination Usage
<a href="https://affiliate.com" rel="sponsored nofollow noopener">
Buy Now (Affiliate Link)
</a>
SEO Impact Analysis
- Link Equity Management
- Follow links: Pass PageRank (internal/external)
- Nofollow: Block equity transfer (saves crawl budget)
- Sponsored/UGC: Identifies non-editorial links
- Google’s Treatment
- Nofollow became “hint” in 2019
- Sponsored/ugc help classify link types
- Still affects crawl priority
Advanced Implementation
- Dynamic Link Handling
<?php if($link['type'] === 'affiliate'): ?>
<a href="<?= $link['url'] ?>" rel="sponsored nofollow"><?= $link['text'] ?></a>
<?php endif; ?>
- Pagination Signals
<link rel="prev" href="/page1">
<link rel="next" href="/page3">
- Resource Hints
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://cdn.example.com">
Common Mistakes
- ❌ Forgetting
noopeneron blank targets - ❌ Overusing nofollow internally
- ❌ Missing sponsored disclosures
- ❌ Inconsistent UGC tagging
- ❌ Broken links with rel attributes
Schema Markup for Rich Snippets
Core Functionality
Schema.org structured data enhances search results by:
- Enabling rich snippets (star ratings, FAQs, events)
- Improving CTR by 10-30%
- Providing explicit content context to search engines
Implementation Methods
- JSON-LD (Recommended)
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Recipe",
"name": "Classic Margherita Pizza",
"image": "pizza.jpg",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Chef Marco"
}
}
</script>
- Microdata
<div itemscope itemtype="https://schema.org/Product">
<span itemprop="name">Blender</span>
<img itemprop="image" src="blender.jpg" alt="Professional blender">
</div>
Key Schema Types
| Type | Rich Result Features | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Article | Headline, date | headline, datePublished |
| Product | Price, rating | offers, review, aggregateRating |
| FAQ | Accordion results | question, acceptedAnswer |
| Breadcrumb | Path navigation | itemListElement |
| Event | Date, location | startDate, location |
Best Practices
- Content Accuracy
- Must match visible page content
- Never include hidden markup
- Keep properties updated
- Technical Requirements
<!-- Placement in <head> for JSON-LD -->
<head>
<script type="application/ld+json">...</script>
</head>
<!-- Body placement for Microdata -->
<body>
<div itemscope>...</div>
</body>
- Testing Tools
- Google Rich Results Test
- Schema Markup Validator (Schema.org)
- Bing Markup Validator
Common Pitfalls
- ❌ Markup/content mismatch
- ❌ Using deprecated properties
- ❌ Missing required fields
- ❌ Duplicate markup implementations
- ❌ Blocking markup with robots.txt
Lazy Loading Attributes for Performance
Core Concept
Lazy loading delays resource loading until needed, providing:
- 20-40% faster initial page loads
- Reduced bandwidth consumption
- Improved Core Web Vitals (LCP, CLS)
Native HTML Implementation
- Basic Image Loading
<img src="hero.jpg" loading="lazy" alt="Main product showcase" width="1200" height="800">
- Iframe Optimization
<iframe src="video.html" loading="lazy" title="Product demo"></iframe>
Technical Specifications
| Attribute | Values | Default | Optimal Use |
|---|---|---|---|
loading |
lazy/eager/auto | browser-dependent | lazy for below-fold content |
decoding |
async/sync/auto | auto | async for non-critical images |
fetchpriority |
high/low/auto | auto | high for LCP elements |
Best Practices
- Strategic Loading
<!-- Above-the-fold (critical) -->
<img src="logo.png" loading="eager" fetchpriority="high" alt="Company logo">
<!-- Below-the-fold -->
<img src="gallery-1.jpg" loading="lazy" alt="Product gallery image 1">
- Viewport Threshold Control
// Adjust loading distance from viewport
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
if('loading' in HTMLImageElement.prototype) {
const images = document.querySelectorAll('img[loading="lazy"]');
images.forEach(img => {
img.fetchPriority = 'low';
img.decoding = 'async';
});
}
});
Common Mistakes
❌ Lazy loading LCP elements
❌ Missing width/height attributes
❌ Overusing loading="eager"
❌ Forgetting mobile viewport considerations
❌ Ignoring browser-specific behaviors
